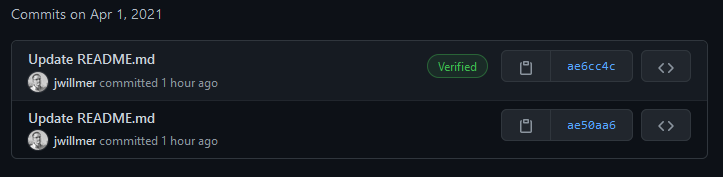
In this post I explain all steps to get the nice green verified flag in GitHub commits when publishing from Windows via GitHub Desktop.
Generate a new GPG key
- Download Gnu PG and install it.
- Open Git bash
- Start generating a key with
gpg --full-generate-key - Use key type
RSA and RSA - Set key size to
4096 - Define how long the key should be valid
- Enter user information
The email must match your verified GitHub email. You can also use the GitHub provided no-reply mail.
- Add a passphrase to secure your key. This needs to be supplied on any commit.
Removing the passphrase from an existing key can be done by setting the password to empty.
$ gpg --list-secret-keys
/home/username/.gnupg/secring.gpg
----------------------------------
sec 4096R/XXXX <creation date>
uid name <email.address>
ssb 4096R/YYYY <creation date>
$ gpg --edit-key XXXX
$ gpg> passwd
Export and backup your public and private key
$ gpg --list-secret-keys -keyid-format LONG
/home/username/.gnupg/secring.gpg
----------------------------------
sec 4096R/XXXX <creation date>
uid name <email.address>
ssb 4096R/YYYY <creation date>
$ gpg --armor --export XXXX
$ gpg --armor --export-secret-key XXXX
Configure your system
-
Create a new PGP key in the user settings of github.com under
SSH and GPG keysand add your public key - Lookup the path of your GPG binary file via
where gpg - Escape the path like this
C:\\Program Files\\Git\\usr\\bin\\gpg.exe - Open your
.gitconfigfile located in your home directory or execute the following command in the command line to open itgit config --global --edit - Add or update the following settings in this file
# YOUR_SIGNING_KEY is the same as you used for exporting your PGP key
[user]
email = YOUR_GITHUB_EMAIL
signingkey = YOUR_SIGNING_KEY
[gpg]
program = GPG_BINARY_PATH
[commit]
gpgsign = true
Now you can start the GitHub Desktop app and commit something. When opening your new commit in GitHub you should see the verify symbol!